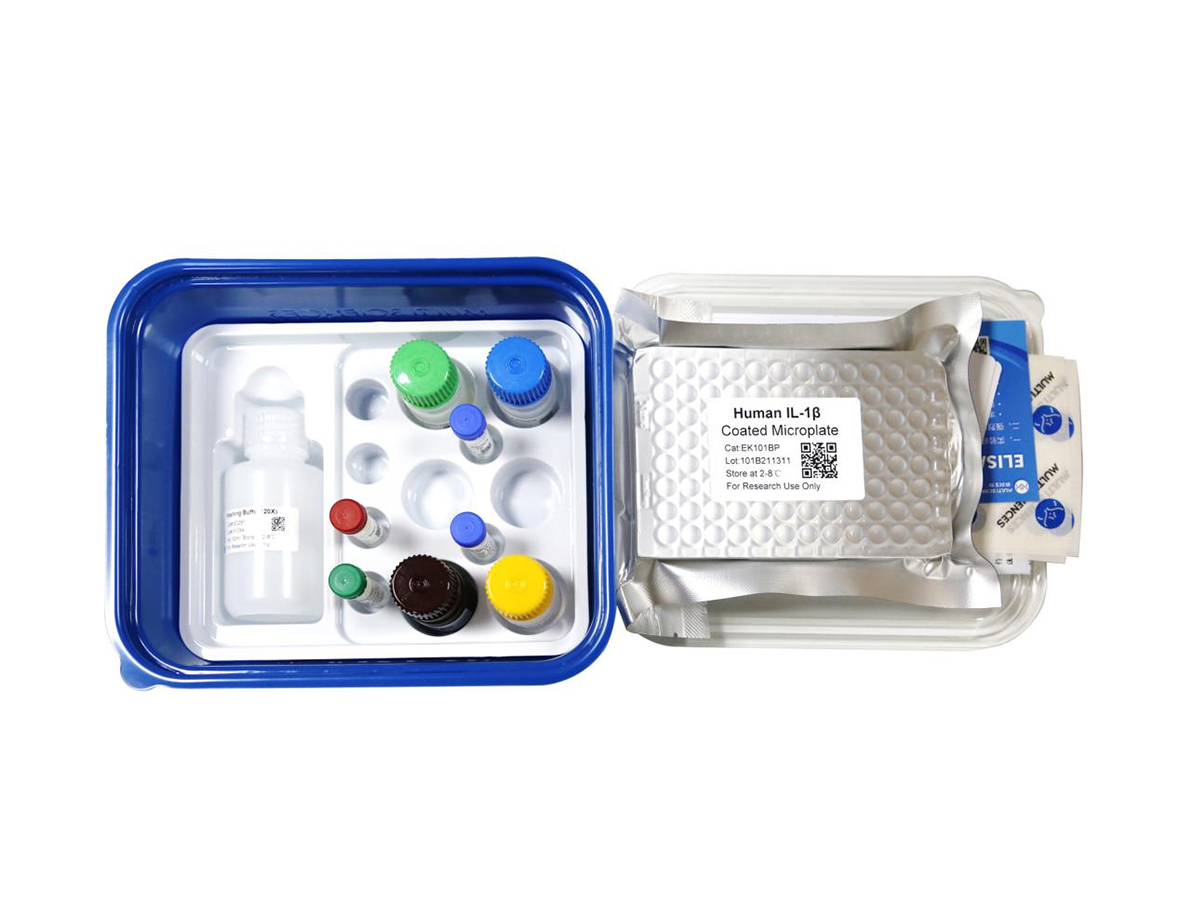
Human MMP-1 ELISA Kit检测试剂盒(酶联免疫吸附法)
¥1,600.00 – ¥2,650.00
因产品会迭代升级,具体实验步骤请按纸质版说明书操作
- 分子靶点:MMP1, CLG
- 种属:人 (Human)
- 样本类型:血清,血浆,细胞培养上清及其他生物学样本
- 检测样本体积:20 μL
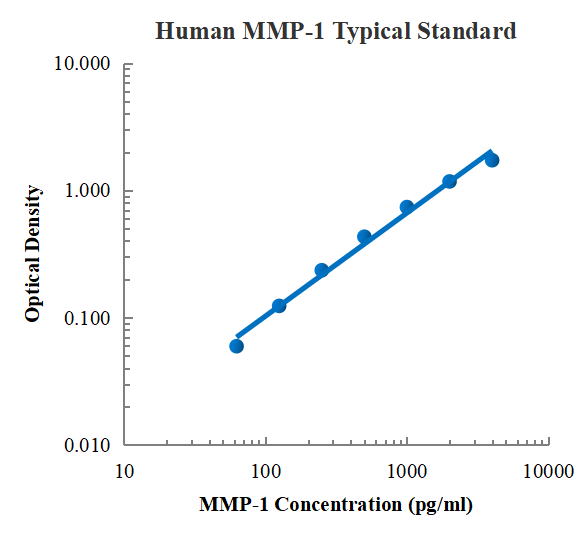
- 灵敏度:11.19 pg/mL
- 检测范围:0.16 ng/mL - 10 ng/mL
- 回收率:83% - 115%
在售SKU:70-EK1M01-48, 70-EK1M01-96
描述
| 商品名 |
Human MMP-1 ELISA Kit (人基质金属蛋白酶1 ELISA试剂盒) |
|---|---|
| 检测方法 |
双抗夹心法 |
| 精密度 |
板内变异系数:2.9% - 4.9%;板间变异系数:3.9% - 4.8% |
| 样本类型 |
血清,血浆,细胞培养上清及其他生物学样本 |
| 检测样本体积 |
20 μL |
| 灵敏度 |
11.19 pg/mL |
| 检测范围 |
0.16 ng/mL - 10 ng/mL |
| 回收率 |
83% - 115% |
| 平均回收率 |
1.07 |
| 板式 |
96孔板,可拆 |
| 保存 |
试剂盒未拆开,4℃保存。已拆开,标准品-20℃保存,其它4℃保存。 |
| 运输条件 |
4℃蓝冰运输 |
| 组分 |
|
检测原理:本试剂盒采用双抗体夹心酶联免疫吸附检测技术。特异性抗人MMP-1抗体预包被在高亲和力的酶标板上。酶标板孔中加入标准品、待测样本和生物素化的检测抗体,经过孵育,样本中存在的MMP-1与固相抗体和检测抗体结合。洗涤去除未结合的物质后,加入辣根过氧化物酶标记的链霉亲和素(Streptavidin-HRP)。洗涤后,加入显色底物TMB,避光显色。颜色反应的深浅与样本中MMP-1的浓度成正比。加入终止液终止反应,在450 nm波长(参考波长5632 nm)测定吸光度值。
分子信息
MMP1 分子靶点信息概述
- 分子名:MMP1, matrix metallopeptidase 1
- 基因家族:Receptor ligands; M10 matrix metallopeptidases
- 曾用名:CLG
- 全称:interstitial collagenase; matrix metalloproteinase 1 (interstitial collagenase)
MMP1 分子靶点综述
基质金属蛋白酶1(MMP-1),又名间质胶原酶和成纤维细胞胶原酶,在人类中由MMP1基因编码。MMP-1由成纤维细胞、软骨细胞、巨噬细胞、角质形成细胞、内皮细胞和成骨细胞产生。其产生受多种刺激物包括细胞因子(如EGF、白细胞介素和TNF-α)和化学物上调,受TIMP-1、TIMP-2和α2-巨球蛋白抑制。MMP-1在细胞外基质重塑中的胶原纤维降解中起重要作用,并参与多种生物过程包括类风湿性关节炎、骨关节炎、牙周病、肿瘤侵袭、血管形成、角膜溃疡、组织重塑、炎症性肠病、动脉粥样硬化和动脉瘤。另外,MMP-1同样也裂解多种底物如酪蛋白、明胶、蛋白聚糖、内功素、促肿瘤坏死因子和软骨连接蛋白。
人 Human MMP1 分子靶点信息
- 分子名:MMP1, matrix metallopeptidase 1
- 别称:
- CLG
- CLGN
- fibroblast collagenase
- interstitial collagenase
- matrix metallopeptidase 1 (interstitial collagenase)
- matrix metalloprotease 1
- matrix metalloproteinase 1
- matrix metalloproteinase 1 (interstitial collagenase)
- 基因序列:NCBI_Gene: 4312
- 蛋白序列:UniProtKB: P03956
人 Human MMP1靶点分子功能(预测)
Enables metalloendopeptidase activity. Involved in cellular response to UV-A; positive regulation of protein-containing complex assembly; and proteolysis. Predicted to be located in extracellular region. Implicated in several diseases, including artery disease (multiple); female reproductive organ cancer (multiple); intrinsic cardiomyopathy (multiple); obstructive lung disease (multiple); and urinary system cancer (multiple). Biomarker of several diseases, including artery disease (multiple); arthritis (multiple); idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis; and systemic lupus erythematosus.
引用文献统计
该产品被引用的文献总数为:12
- Forsythiaside A Regulates Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells by Inhibiting NOX4-Dependent ROS
影响因子:7.31刊物:Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity发表日期:2022/1/5 - Elevated microRNA‑145‑5p increases matrix metalloproteinase‑9 by activating the nuclear factor‑κB pathway in rheumatoid arthritis
影响因子:1.851刊物:Molecular Medicine Reports发表日期:2019/7/15 - Follistatin-like protein 1 induction of matrix metalloproteinase 1, 3 and 13 gene expression in rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes requires MAPK, JAK/STAT3 and NF-κB pathways
影响因子:3.923刊物:JOURNAL OF CELLULAR PHYSIOLOGY发表日期:2018/6/22 - Protective effects of Clematichinenoside AR against inflammation and cytotoxicity induced by human tumor necrosis factor-α
影响因子:3.361刊物:INTERNATIONAL IMMUNOPHARMACOLOGY发表日期:2019/8/10 - Escape from abluminal LRP1-mediated clearance for boosted nanoparticle brain delivery and brain metastasis treatment
影响因子:7.097刊物:Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B发表日期:2020/10/21 - Comparison of the therapeutic effects of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells and adipose-derived stem cells on erectile dysfunction in a rat model of bilateral cavernous nerve injury.
影响因子:6.064刊物:Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology发表日期:2022/10/7 - Baicalein inhibits inflammatory response and promotes osteogenic activity in periodontal ligament cells challenged with lipopolysaccharides
刊物:BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies发表日期:2021/1/23 - Antioxidant glutathione inhibits inflammation in synovial fibroblasts via PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway: An in vitro study
刊物:Archives of Rheumatology发表日期:2021/12/24 - Aconiti Lateralis Radix Praeparata lipid-soluble alkaloids alleviates IL-1β-induced inflammation of human fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis by inhibiting NF-κB and MAPKs signaling pathways and inducing apoptosis
影响因子:3.926刊物:CYTOKINE发表日期:2022/1/29 - Supramolecular collagen nanoparticles for anti-wrinkle, skin whitening, and moisturizing effects
影响因子:5.4刊物:COLLOIDS AND SURFACES B-BIOINTERFACES发表日期:2024-09-28 - Knockdown of Galectin-9 alleviates rheumatoid arthritis through suppressing TNF-α-induced activation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes
影响因子:5.8刊物:BIOCHEMICAL PHARMACOLOGY发表日期:2023-12-21 - Protective Effects of Clematichinenoside Ar against Inflammation and Cytotoxicity Induced by Human Tumor Necrosis Factor-Α
刊物:International immunopharmacology 75, 105563 (2019)
未设置相关文章分类。
操作步骤
文章目录[隐藏]
- ELISA操作常见问题
- 小心!你的 ELISA 试剂盒可能是假的
- 开学学习计划,如何收集ELISA检测样本——细胞
- 开学学习计划,如何选择ELISA试剂盒
- 开学学习计划,ELISA从新手到入门!
- 一文掌握ELISA实验显色判断、数据分析及标曲拟合
- 血清OR血浆,哪个是ELISA的菜
- ELISA通关必备丨数据篇丨标准曲线不佳
- ELISA通关必备丨操作篇丨常见问题及解决方案
- ELISA通关必备丨操作篇丨溶解与稀释标准品
- ELISA通关必备丨样本篇丨不常见样本
- ELISA通关必备丨样本篇丨常见样本丨细胞
- ELISA通关必备丨如何选择试剂盒
- ELISA通关必备丨基础知识
- 真?假?ELISA试剂盒选择要小心
- ELISA常见类型一 | 双抗夹心法,你要的都在这里!
- ELISA常见类型二 | 竞争法,五分钟搞定!
- 叮!联科向您投递了个ELISA实验操作干货包,请查收~
- 【视频】ELISA实验操作步骤演示视频教程
- ELISA 组织样本的处理—大鼠组织
- 【视频】ELISA实验原理与常见问题分析
- 查看更多ELISA操作相关问题
ELISA操作常见问题
查看更多ELISA操作相关问题
引用文献
文章目录[隐藏]
- Forsythiaside A Regulates Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells by Inhibiting NOX4-Dependent ROS
- Elevated microRNA‑145‑5p increases matrix metalloproteinase‑9 by activating the nuclear factor‑κB pathway in rheumatoid arthritis
- Follistatin-like protein 1 induction of matrix metalloproteinase 1, 3 and 13 gene expression in rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes requires MAPK, JAK/STAT3 and NF-κB pathways
- Protective effects of Clematichinenoside AR against inflammation and cytotoxicity induced by human tumor necrosis factor-α
- Escape from abluminal LRP1-mediated clearance for boosted nanoparticle brain delivery and brain metastasis treatment
- Comparison of the therapeutic effects of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells and adipose-derived stem cells on erectile dysfunction in a rat model of bilateral cavernous nerve injury.
- Baicalein inhibits inflammatory response and promotes osteogenic activity in periodontal ligament cells challenged with lipopolysaccharides
- Antioxidant glutathione inhibits inflammation in synovial fibroblasts via PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway: An in vitro study
- Aconiti Lateralis Radix Praeparata lipid-soluble alkaloids alleviates IL-1β-induced inflammation of human fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis by inhibiting NF-κB and MAPKs signaling pathways and inducing apoptosis
- Supramolecular collagen nanoparticles for anti-wrinkle, skin whitening, and moisturizing effects
- Knockdown of Galectin-9 alleviates rheumatoid arthritis through suppressing TNF-α-induced activation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes
- Protective Effects of Clematichinenoside Ar against Inflammation and Cytotoxicity Induced by Human Tumor Necrosis Factor-Α
Forsythiaside A Regulates Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells by Inhibiting NOX4-Dependent ROS
Elevated microRNA‑145‑5p increases matrix metalloproteinase‑9 by activating the nuclear factor‑κB pathway in rheumatoid arthritis
Follistatin-like protein 1 induction of matrix metalloproteinase 1, 3 and 13 gene expression in rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes requires MAPK, JAK/STAT3 and NF-κB pathways
Protective effects of Clematichinenoside AR against inflammation and cytotoxicity induced by human tumor necrosis factor-α
Escape from abluminal LRP1-mediated clearance for boosted nanoparticle brain delivery and brain metastasis treatment
Comparison of the therapeutic effects of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells and adipose-derived stem cells on erectile dysfunction in a rat model of bilateral cavernous nerve injury.
Baicalein inhibits inflammatory response and promotes osteogenic activity in periodontal ligament cells challenged with lipopolysaccharides
Antioxidant glutathione inhibits inflammation in synovial fibroblasts via PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway: An in vitro study
Aconiti Lateralis Radix Praeparata lipid-soluble alkaloids alleviates IL-1β-induced inflammation of human fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis by inhibiting NF-κB and MAPKs signaling pathways and inducing apoptosis
Supramolecular collagen nanoparticles for anti-wrinkle, skin whitening, and moisturizing effects
Knockdown of Galectin-9 alleviates rheumatoid arthritis through suppressing TNF-α-induced activation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes
Protective Effects of Clematichinenoside Ar against Inflammation and Cytotoxicity Induced by Human Tumor Necrosis Factor-Α