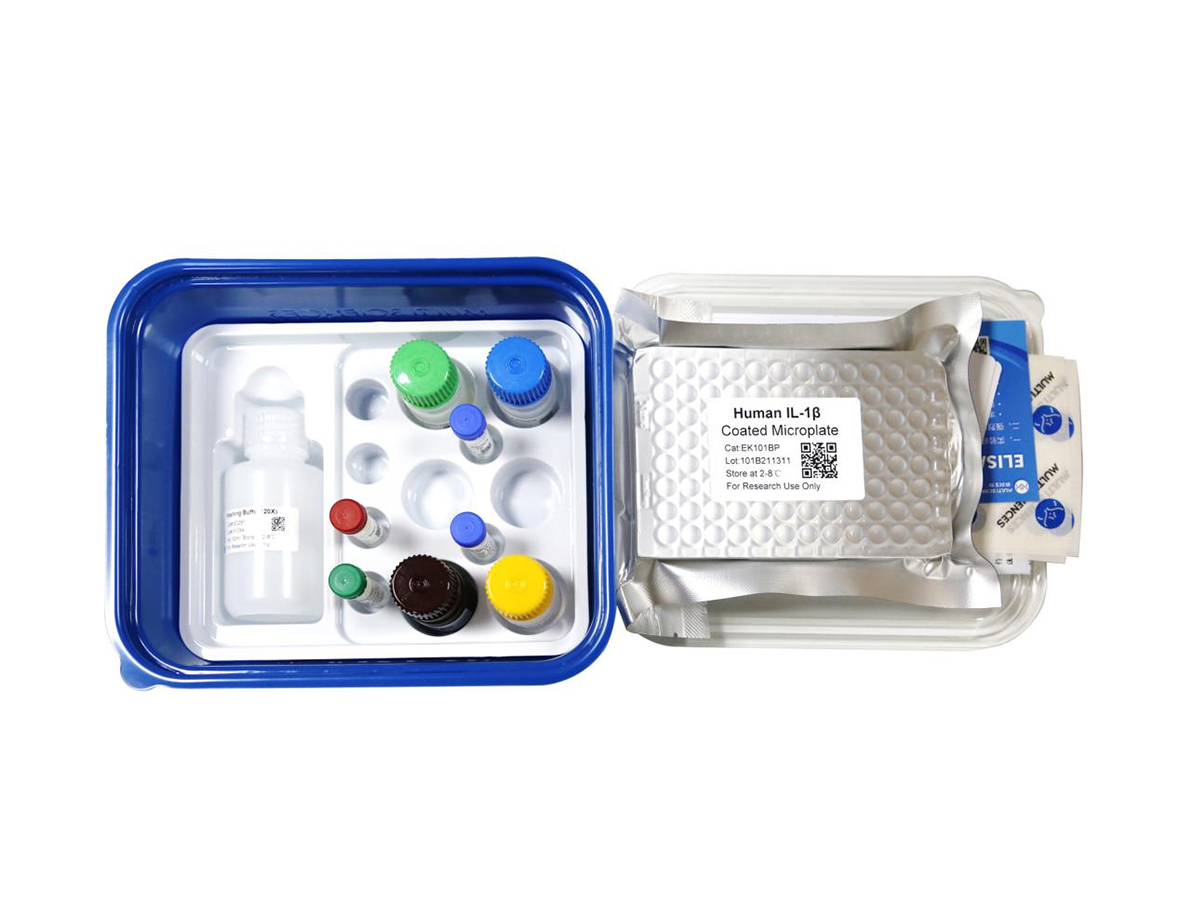
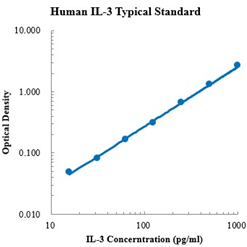
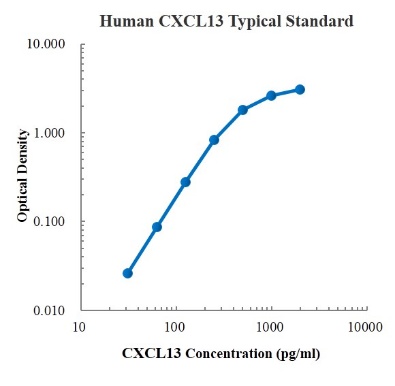
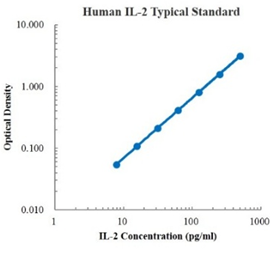
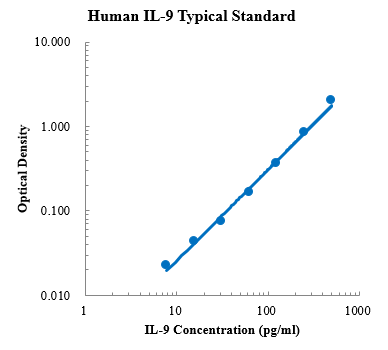
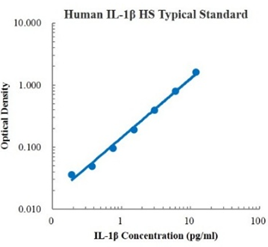
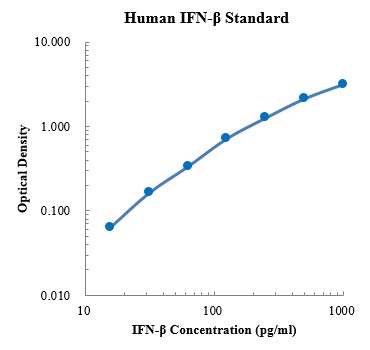
Human IFN-β Standard (人 IFN-β 标准品)
¥180.00
描述
文章目录[隐藏]
本产品只包含标准品试剂,如需购买试剂盒请点击下图
-
- EK1236 25 Citations
- ELISA试剂盒
Human IFN-β ELISA Kit检测试剂盒(酶联免疫吸附法)
- ¥1,600.00 – ¥2,650.00
| 商品名 |
Human IFN-β Standard (人 IFN-β 标准品) |
|---|---|
| 组分 |
人IFN-β标准品 |
| 检测方法 |
双抗夹心法 |
| 样本类型 |
血清,血浆,细胞培养上清及其他生物学样本 |
| 板式 |
管 |
| 保存 |
短期4℃,长期-20℃保存 |
| 运输条件 |
4℃蓝冰运输 |
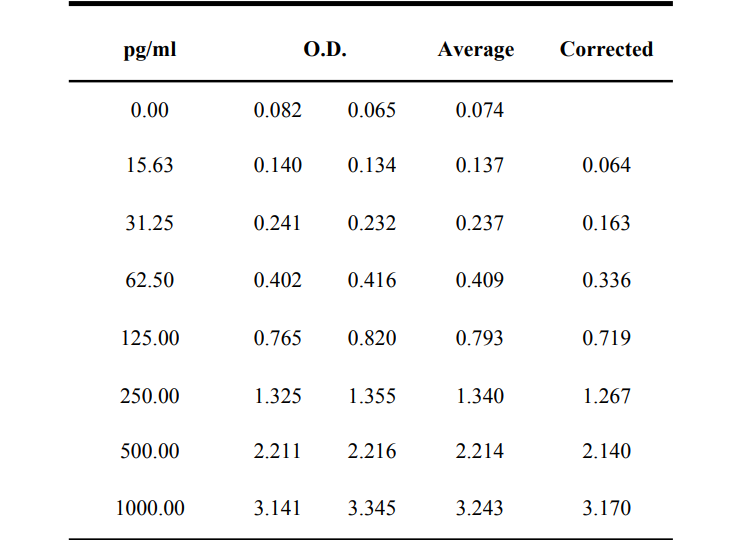
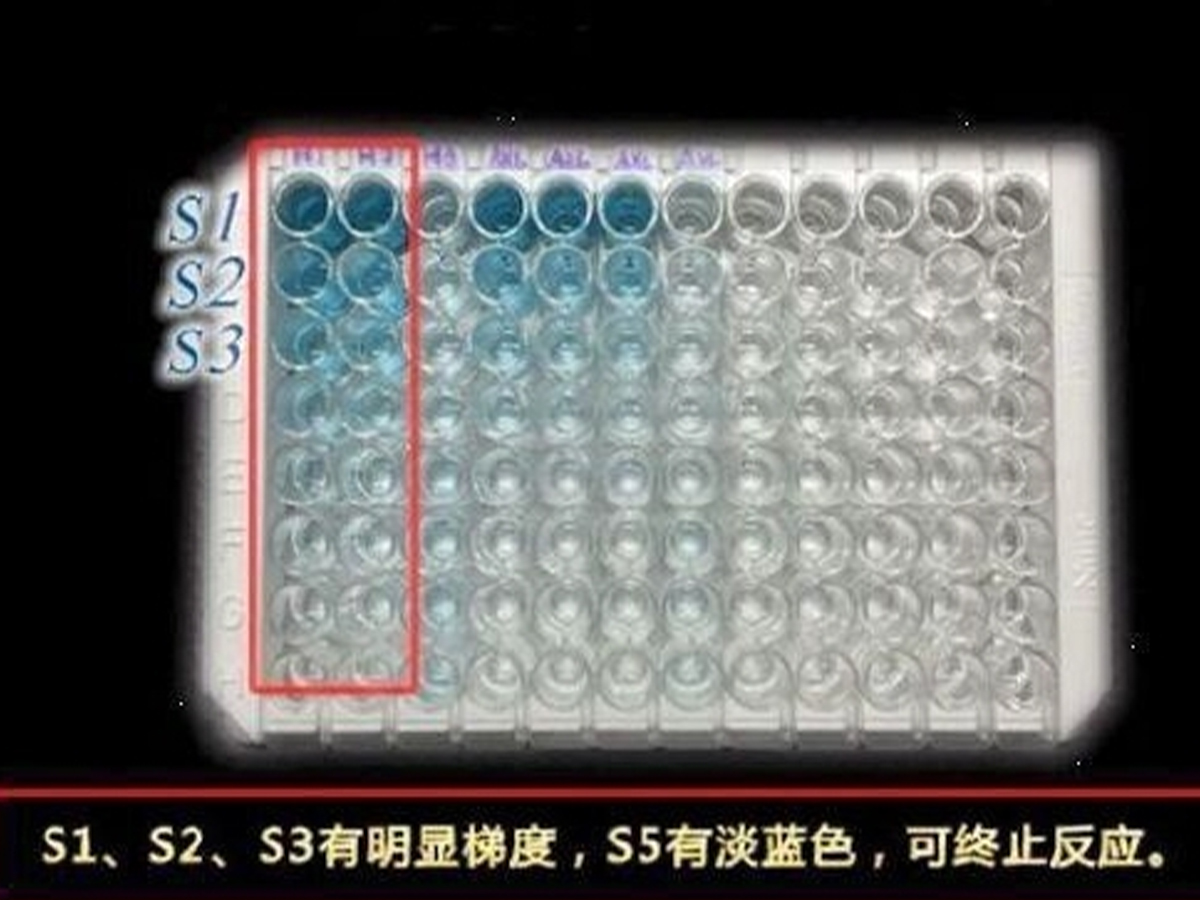
检测原理:本试剂盒采用双抗体夹心酶联免疫吸附检测技术。特异性抗人IFN-β抗体预包被在高亲和力的酶标板上。酶标板孔中加入标准品、待测样本和生物素化的检测抗体,经过孵育,样本中存在的IFN-β与固相抗体和检测抗体结合。洗涤去除未结合的物质后,加入辣根过氧化物酶标记的链霉亲和素(Streptavidin-HRP)。洗涤后,加入显色底物TMB,避光显色。颜色反应的深浅与样本中IFN-β的浓度成正比。加入终止液终止反应,在450 nm波长(参考波长570 - 630 nm)测定吸光度值。
分子信息
IFNB1 分子靶点信息概述
- 分子名:IFNB1, interferon beta 1
- 基因家族:Interferons
- 别名:IFB; IFF
- 曾用名:IFNB
- 全称:interferon, beta 1, fibroblast
IFNB1 分子靶点综述
干扰素(IFNs)是宿主细胞在响应病原体(如病毒、细菌、寄生虫或者肿瘤细胞)时合成和释放的一组信号蛋白。在通常情况下,病毒感染的细胞会释放干扰素,使周围的细胞提高其抗病毒防御能力。基于受体类型,人类干扰素可分为3大类型:I型干扰素,包括IFN-α、IFN-β、IFN-ε、IFN-κ和IFN-ω,II型干扰素(在人类中称为IFN-γ)和III型干扰素。IFN-β通过信号通路STAT1和STAT2上调和下调多种基因,其中,大部分基因参与抗病毒免疫反应。IFN-β在诱导广泛的非特异性抗病毒感染中起重要作用,它还影响细胞增殖并调节免疫应答。
人 Human IFNB1 分子靶点信息
- 分子名:IFNB1, interferon beta 1
- 别称:
- fibroblast interferon
- IFB
- IFF
- IFN-beta
- IFNB
- interferon beta
- interferon-beta
- interferon, beta 1
- interferon, beta 1, fibroblast
- MGC96956
- 基因序列:NCBI_Gene: 3456
- 蛋白序列:UniProtKB: P01574
人 Human IFNB1靶点分子功能(预测)
Enables chloramphenicol O-acetyltransferase activity and cytokine activity. Involved in several processes, including cellular response to cytokine stimulus; negative regulation of T-helper 2 cell cytokine production; and positive regulation of nitrogen compound metabolic process. Acts upstream of or within response to exogenous dsRNA. Predicted to be located in extracellular region. Predicted to be active in extracellular space. Implicated in COVID-19.
引用文献统计
该产品被引用的文献总数为:0
暂无相关文献引用。
ELISA标准品操作常见问题查看更多ELISA标准品操作步骤技术文章
查看更多ELISA标准品操作步骤技术文章
操作步骤
文章目录[隐藏]
- ELISA操作常见问题
- 小心!你的 ELISA 试剂盒可能是假的
- 开学学习计划,如何收集ELISA检测样本——细胞
- 开学学习计划,如何选择ELISA试剂盒
- 开学学习计划,ELISA从新手到入门!
- 一文掌握ELISA实验显色判断、数据分析及标曲拟合
- 血清OR血浆,哪个是ELISA的菜
- ELISA通关必备丨数据篇丨标准曲线不佳
- ELISA通关必备丨操作篇丨常见问题及解决方案
- ELISA通关必备丨操作篇丨溶解与稀释标准品
- ELISA通关必备丨样本篇丨不常见样本
- ELISA通关必备丨样本篇丨常见样本丨细胞
- ELISA通关必备丨如何选择试剂盒
- ELISA通关必备丨基础知识
- 真?假?ELISA试剂盒选择要小心
- ELISA常见类型一 | 双抗夹心法,你要的都在这里!
- ELISA常见类型二 | 竞争法,五分钟搞定!
- 叮!联科向您投递了个ELISA实验操作干货包,请查收~
- 【视频】ELISA实验操作步骤演示视频教程
- ELISA 组织样本的处理—大鼠组织
- 【视频】ELISA实验原理与常见问题分析
- 查看更多ELISA操作相关问题
ELISA操作常见问题
查看更多ELISA操作相关问题
引用文献
文章目录[隐藏]
- Cathelicidin antimicrobial peptides suppress EV71 infection via regulating antiviral response and inhibiting viral binding
- Lonidamine potentiates the oncolytic efficiency of M1 virus independent of hexokinase 2 but via inhibition of antiviral immunity
- Immune Checkpoint Inhibition Overcomes ADCP-Induced Immunosuppression by Macrophages
- Oroxylin A regulates cGAS DNA hypermethylation induced by methionine metabolism to promote HSC senescence
- Allosteric inhibition reveals SHP2-mediated tumor immunosuppression in colon cancer by single-cell transcriptomics
- LncNSPL facilitates influenza A viral immune escape by restricting TRIM25-mediated K63-linked RIG-I ubiquitination
- A C-terminal glutamine recognition mechanism revealed by E3 ligase TRIM7 structures
- Structural insights into a shared mechanism of human STING activation by a potent agonist and an autoimmune disease-associated mutation
- Single-cell landscape of immunological responses in patients with COVID-19
- Anemoside B4 inhibits enterovirus 71 propagation in mice through upregulating 14-3-3 expression and type I interferon responses
- Lipopolysaccharide enhances DNA‑induced IFN‑β expression and autophagy by upregulating cGAS expression in A549 cells
- RIPK3-Dependent Necroptosis Is Induced and Restricts Viral Replication in Human Astrocytes Infected With Zika Virus
- Allicin Inhibits Proliferation by Decreasing IL-6 and IFN-β in HCMV-Infected Glioma Cells
- STING agonist cGAMP enhances anti-tumor activity of CAR-NK cells against pancreatic cancer
- Targeted Delivery of STING Agonist via Albumin Nanoreactor Boosts Immunotherapeutic Efficacy against Aggressive Cancers
- Exploring expression levels of the cGAS-STING pathway genes in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of spinal tuberculosis patients
- STING-mediated IL-6 Inhibits OATP1B1 Expression via the TCF4 Signaling Pathway in Cholestasis
- TRIM38 Induced in Respiratory Syncytial Virus-infected Cells Downregulates Type I Interferon Expression by Competing with TRIM25 to Bind RIG-I
- Luteolin-7-O-glucoside promotes macrophage release of IFN-β by maintaining mitochondrial function and corrects the disorder of glucose metabolism during RSV infection
- RNA methyltransferase FTSJ3 regulates the type I interferon pathway to promote hepatocellular carcinoma immune evasion
- Human endogenous retroviruses as epigenetic therapeutic targets in TP53-mutated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- The RNA-Splicing Ligase RTCB Promotes Influenza A Virus Replication by Suppressing Innate Immunity via Interaction with RNA Helicase DDX1
- IFN-beta and EIF2AK2 are potential biomarkers for interstitial lung disease in anti-MDA5 positive dermatomyositis
- Anemoside B4 inhibits enterovirus 71 propagation in mice through upregulating 14-3-3 expression and type I interferon responses
- Lipopolysaccharide Enhances DNA-Induced Ifn-Β Expression and Autophagy by Upregulating Cgas Expression in A549 Cells
Cathelicidin antimicrobial peptides suppress EV71 infection via regulating antiviral response and inhibiting viral binding
Lonidamine potentiates the oncolytic efficiency of M1 virus independent of hexokinase 2 but via inhibition of antiviral immunity
Immune Checkpoint Inhibition Overcomes ADCP-Induced Immunosuppression by Macrophages
Oroxylin A regulates cGAS DNA hypermethylation induced by methionine metabolism to promote HSC senescence
Allosteric inhibition reveals SHP2-mediated tumor immunosuppression in colon cancer by single-cell transcriptomics
LncNSPL facilitates influenza A viral immune escape by restricting TRIM25-mediated K63-linked RIG-I ubiquitination
A C-terminal glutamine recognition mechanism revealed by E3 ligase TRIM7 structures
Structural insights into a shared mechanism of human STING activation by a potent agonist and an autoimmune disease-associated mutation
Single-cell landscape of immunological responses in patients with COVID-19
Anemoside B4 inhibits enterovirus 71 propagation in mice through upregulating 14-3-3 expression and type I interferon responses
Lipopolysaccharide enhances DNA‑induced IFN‑β expression and autophagy by upregulating cGAS expression in A549 cells
RIPK3-Dependent Necroptosis Is Induced and Restricts Viral Replication in Human Astrocytes Infected With Zika Virus
Allicin Inhibits Proliferation by Decreasing IL-6 and IFN-β in HCMV-Infected Glioma Cells
STING agonist cGAMP enhances anti-tumor activity of CAR-NK cells against pancreatic cancer
Targeted Delivery of STING Agonist via Albumin Nanoreactor Boosts Immunotherapeutic Efficacy against Aggressive Cancers
Exploring expression levels of the cGAS-STING pathway genes in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of spinal tuberculosis patients
STING-mediated IL-6 Inhibits OATP1B1 Expression via the TCF4 Signaling Pathway in Cholestasis
TRIM38 Induced in Respiratory Syncytial Virus-infected Cells Downregulates Type I Interferon Expression by Competing with TRIM25 to Bind RIG-I
Luteolin-7-O-glucoside promotes macrophage release of IFN-β by maintaining mitochondrial function and corrects the disorder of glucose metabolism during RSV infection
RNA methyltransferase FTSJ3 regulates the type I interferon pathway to promote hepatocellular carcinoma immune evasion
Human endogenous retroviruses as epigenetic therapeutic targets in TP53-mutated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
The RNA-Splicing Ligase RTCB Promotes Influenza A Virus Replication by Suppressing Innate Immunity via Interaction with RNA Helicase DDX1
IFN-beta and EIF2AK2 are potential biomarkers for interstitial lung disease in anti-MDA5 positive dermatomyositis
- 细胞培养上清
Anemoside B4 inhibits enterovirus 71 propagation in mice through upregulating 14-3-3 expression and type I interferon responses
Lipopolysaccharide Enhances DNA-Induced Ifn-Β Expression and Autophagy by Upregulating Cgas Expression in A549 Cells