http://www.liankebio.com/article-information_Newsletter-2631.html
作者:联科生物 发布日期:2019-07-10 08:30
|
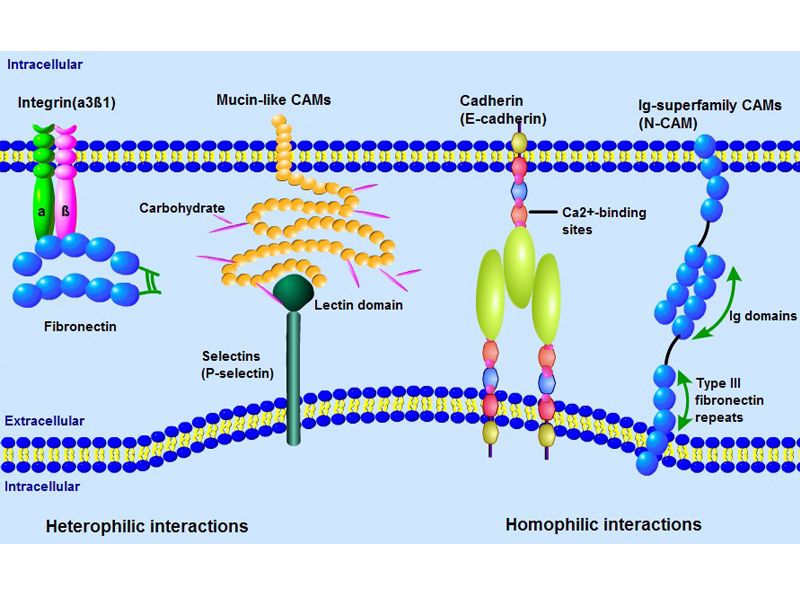
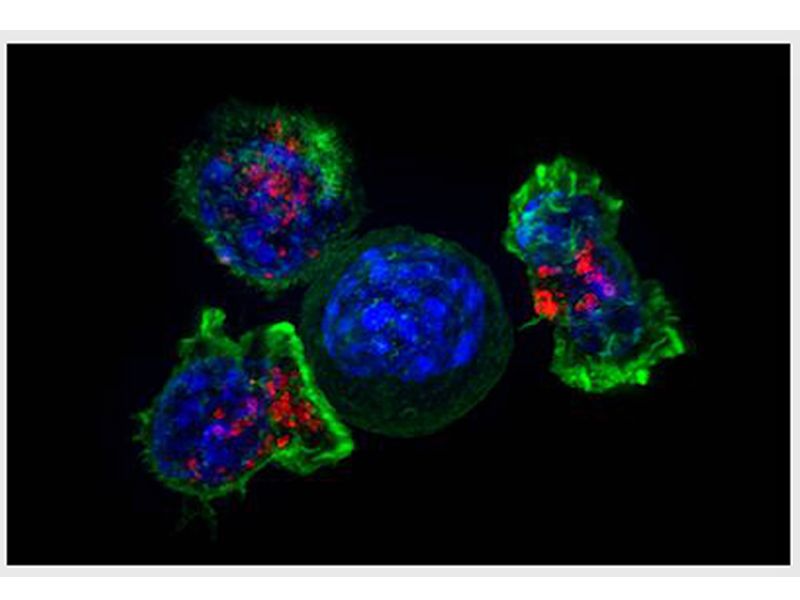
类风湿关节炎(Rheumatoida Rthritis,RA)是一种以慢性、进行性、侵蚀性为特征的自身免疫性疾病。RA主要是自身抗原被主要组织相容性复合体II(MHC—lI)型阳性的抗原呈递细胞(APC)呈递给活化CD4+T细胞,启动特异性免疫应答;同时活化的T细胞、巨噬细胞等向滑膜迁移,使多种炎性细胞因子如TNF、IL-1和IL-6等分泌增多,浸润滑膜关节,导致相应关节炎症状。近年来对RA免疫机制的研究占首要地位,发现众多细胞因子。 今天介绍2个前沿靶标: RA患者血清、关节滑液中IL-1水平高低与RA临床活动性明显相关。IL-1β是RA软骨破坏的重要原因之一,能分泌到细胞膜的外面,作用于其他细胞发挥效应,而IL-1α只能发挥自分泌信使的功能,致炎性较弱。
参考文献: 2. Articular inflammation is controlled by myeloidcell-derived interleukin 1 receptor antagonist during the acute phase of arthritis in mice[J]. Ann Rheum Dis,2012:71:281–287. IF=12.24 3. Articular inflammation is controlled by myeloid cell-derived interleukin 1 receptor antagonist during the acute phase of arthritis in mice[J].Ann Rheum Dis 2012;71:281–287. IF=12.24 4. MiR-20a regulates ASK1 expression and TLR4-dependent cytokine release in rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes[J].Ann Rheum Dis,2013;72:1071–1079. IF=12.24 5. The dual inhibitor of lipoxygenase and cyclooxygenase ML3000 decreases the expression of CXCR3 ligands[J]. Ann Rheum Dis 2008;67:524–529. IF= IF=12.24 |


 CXCL10/IP-10:
CXCL10/IP-10: 联科生物相关产品:24/48/96T 均有
联科生物相关产品:24/48/96T 均有