Human EGF Standard (人表皮生长因子体 标准品)
¥180.00
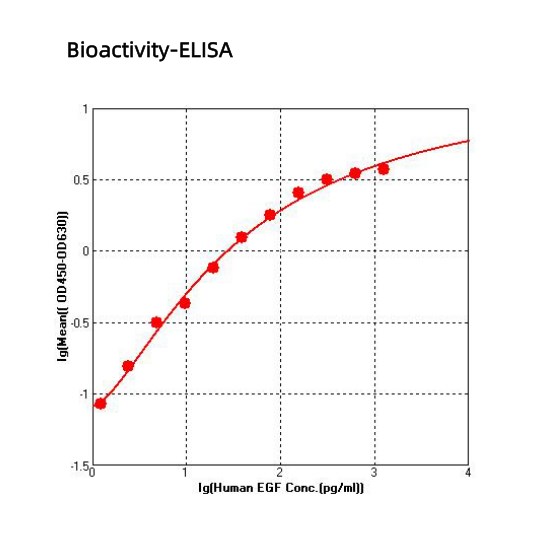
- 分子靶点:EGF, epidermal growth factor
- 种属:人 (Human)
- 试剂盒:EK193
- 保存:短期4℃保存,长期-20℃保存
- 运输条件:4℃蓝冰运输
在售SKU:70-EK193S
文章目录[隐藏]
本产品只包含标准品试剂,如需购买试剂盒请点击下图
-
- EK193 12 Citations
- ELISA试剂盒
Human EGF ELISA Kit检测试剂盒(酶联免疫吸附法)
- ¥1,600.00 – ¥2,650.00
| 商品名 |
Human EGF Standard (人表皮生长因子体 标准品) |
|---|---|
| 组分 |
人EGF标准品 |
| 板式 |
管 |
| 保存 |
短期4℃,长期-20℃保存 |
| 运输条件 |
4℃蓝冰运输 |
分子信息
EGF 分子靶点信息概述
- 分子名:EGF, epidermal growth factor
- 全称:Pro-epidermal growth factor; epidermal growth factor (beta-urogastrone)
EGF 分子靶点综述
表皮生长因子(EGF)是一种通过与其受体EGFR结合,刺激细胞生长、增殖和分化的生长因子。EGF是小分子量多肽,最迟从小鼠下颌下腺纯化得到,随后在很多人的组织中均有发现,包括下颌下腺和腮腺。由饮食中的无机碘调控的唾液EGF在维持奥罗食管和胃组织健全方面具有重要的生理作用。唾液EGF的生理作用包括治愈口腔和胃溃疡、抑制胃酸分泌、刺激DNA合成以及保护粘膜免受腔内有害因素(如胃酸、胆汁酸、胃蛋白酶和胰蛋白酶)和物理、化学和细菌因素破坏。在某些通常与受体的突变和功能异常(如不依赖于EGF水平或与EGF结合的组成性受体信号传导)有关的癌症中,可观察到EGF受体活性增强。
人 Human EGF 分子靶点信息
- 分子名:EGF, epidermal growth factor
- 别称:
- beta-urogastrone
- HOMG4
- pro-epidermal growth factor
- URG
- 基因序列:NCBI_Gene: 1950
- 蛋白序列:UniProtKB: P01133
人 Human EGF靶点分子功能(预测)
Enables growth factor activity and guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity. Involved in several processes, including ERK1 and ERK2 cascade; positive regulation of macromolecule metabolic process; and positive regulation of signal transduction. Acts upstream of or within positive regulation of cell population proliferation. Located in extracellular exosome. Implicated in several diseases, including Zollinger-Ellison syndrome; hepatobiliary system cancer (multiple); high grade glioma (multiple); lung non-small cell carcinoma (multiple); and primary hypomagnesemia (multiple). Biomarker of several diseases, including acute kidney failure; lupus nephritis; neurodegenerative disease (multiple); pancreatic cancer (multiple); and pancreatitis.
引用文献统计
该产品被引用的文献总数为:1
ELISA标准品操作常见问题查看更多ELISA标准品操作步骤技术文章
查看更多ELISA标准品操作步骤技术文章
操作步骤
文章目录[隐藏]
- ELISA操作常见问题
- 小心!你的 ELISA 试剂盒可能是假的
- 开学学习计划,如何收集ELISA检测样本——细胞
- 开学学习计划,如何选择ELISA试剂盒
- 开学学习计划,ELISA从新手到入门!
- 一文掌握ELISA实验显色判断、数据分析及标曲拟合
- 血清OR血浆,哪个是ELISA的菜
- ELISA通关必备丨数据篇丨标准曲线不佳
- ELISA通关必备丨操作篇丨常见问题及解决方案
- ELISA通关必备丨操作篇丨溶解与稀释标准品
- ELISA通关必备丨样本篇丨不常见样本
- ELISA通关必备丨样本篇丨常见样本丨细胞
- ELISA通关必备丨如何选择试剂盒
- ELISA通关必备丨基础知识
- 真?假?ELISA试剂盒选择要小心
- ELISA常见类型一 | 双抗夹心法,你要的都在这里!
- ELISA常见类型二 | 竞争法,五分钟搞定!
- 叮!联科向您投递了个ELISA实验操作干货包,请查收~
- 【视频】ELISA实验操作步骤演示视频教程
- ELISA 组织样本的处理—大鼠组织
- 【视频】ELISA实验原理与常见问题分析
- 查看更多ELISA操作相关问题
ELISA操作常见问题
查看更多ELISA操作相关问题
引用文献
文章目录[隐藏]
- Tumor associated neutrophils promote the metastasis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorate Skin Aging of Nude Mice Through Autophagy-Mediated Anti-Senescent Mechanism
- Expression of miR-182 in patients with fracture of tibial plateau and its regulative effects on the fracture healing
- FOXA1 promotes prostate cancer angiogenesis by inducing multiple pro-angiogenic factors expression
- Autocrine TGF-alpha is associated with Benzo(a)pyrene-induced mucus production and MUC5AC expression during allergic asthma
- Growth factors-based platelet lysate rejuvenates skin against ageing through NF-κB signalling pathway: In vitro and in vivo mechanistic and clinical studies
- Transverse Tibial Bone Transport Enhances Distraction Osteogenesis and Vascularization in the Treatment of Diabetic Foot
- Utilizing 3D bioprinted platelet-rich fibrin-based materials to promote the regeneration of oral soft tissue
- Advanced-platelet-rich fibrin extract promotes adipogenic and osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells in a dose-dependent manner in vitro
- Growth factors-based beneficial effects of platelet lysate on umbilical cord-derived stem cells and their synergistic use in osteoarthritis treatment
- Transcription Factor SOX18 Promotes Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Progression and Alleviates Cabozantinib-Mediated Inhibitory Effects
- KLF5/MDM2 Axis Modulates Oxidative Stress and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Human Lens Epithelial Cells: The Role In Diabetic Cataract
Tumor associated neutrophils promote the metastasis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Human Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorate Skin Aging of Nude Mice Through Autophagy-Mediated Anti-Senescent Mechanism
Expression of miR-182 in patients with fracture of tibial plateau and its regulative effects on the fracture healing
FOXA1 promotes prostate cancer angiogenesis by inducing multiple pro-angiogenic factors expression
Autocrine TGF-alpha is associated with Benzo(a)pyrene-induced mucus production and MUC5AC expression during allergic asthma
Growth factors-based platelet lysate rejuvenates skin against ageing through NF-κB signalling pathway: In vitro and in vivo mechanistic and clinical studies
Transverse Tibial Bone Transport Enhances Distraction Osteogenesis and Vascularization in the Treatment of Diabetic Foot
Utilizing 3D bioprinted platelet-rich fibrin-based materials to promote the regeneration of oral soft tissue
Advanced-platelet-rich fibrin extract promotes adipogenic and osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells in a dose-dependent manner in vitro
Growth factors-based beneficial effects of platelet lysate on umbilical cord-derived stem cells and their synergistic use in osteoarthritis treatment
Transcription Factor SOX18 Promotes Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Progression and Alleviates Cabozantinib-Mediated Inhibitory Effects
KLF5/MDM2 Axis Modulates Oxidative Stress and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Human Lens Epithelial Cells: The Role In Diabetic Cataract