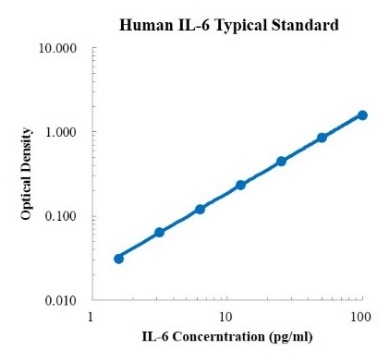
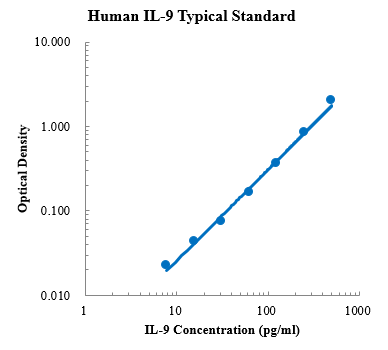
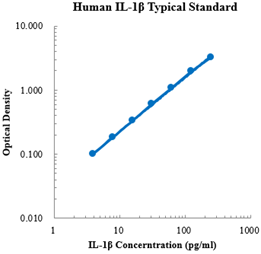
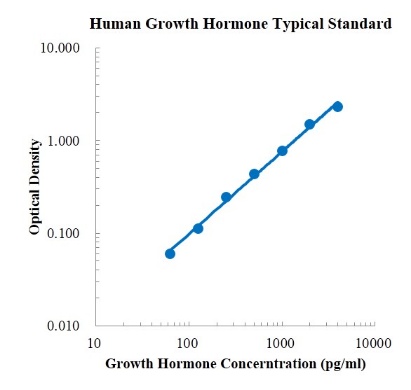
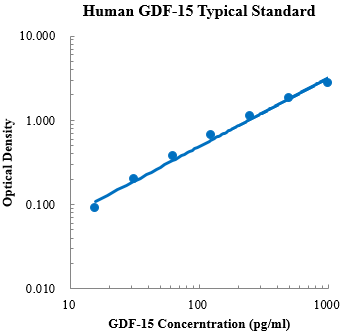
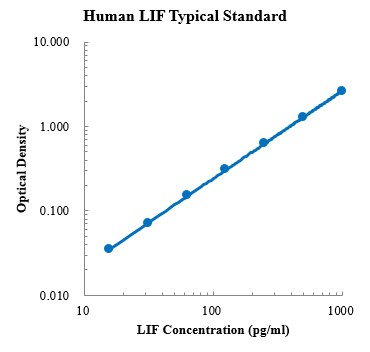
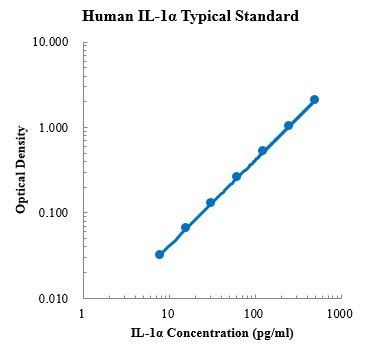
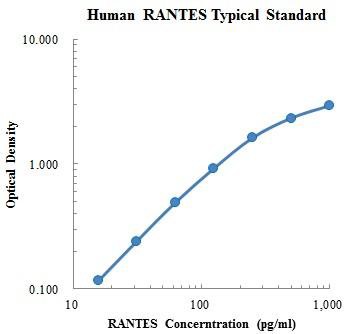
Human CCL5/RANTES Standard (人趋化因子配体5 标准品)
¥180.00
描述
文章目录[隐藏]
本产品只包含标准品试剂,如需购买试剂盒请点击下图
-
- EK1129 23 Citations
- ELISA试剂盒
Human CCL5/RANTES ELISA Kit检测试剂盒(酶联免疫吸附法)
- ¥1,600.00 – ¥2,650.00
| 商品名 |
Human CCL5/RANTES Standard (人趋化因子配体5 标准品) |
|---|---|
| 组分 |
人CCL5/RANTESA 标准品 |
| 检测方法 |
双抗夹心法 |
| 样本类型 |
血清,血浆,细胞培养上清及其他生物学样本 |
| 板式 |
管 |
| 保存 |
短期4℃,长期-20℃保存 |
| 运输条件 |
4℃蓝冰运输 |
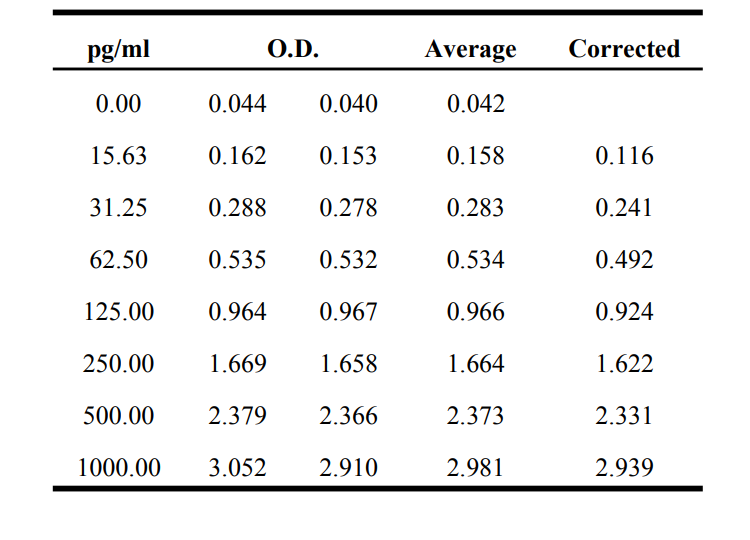
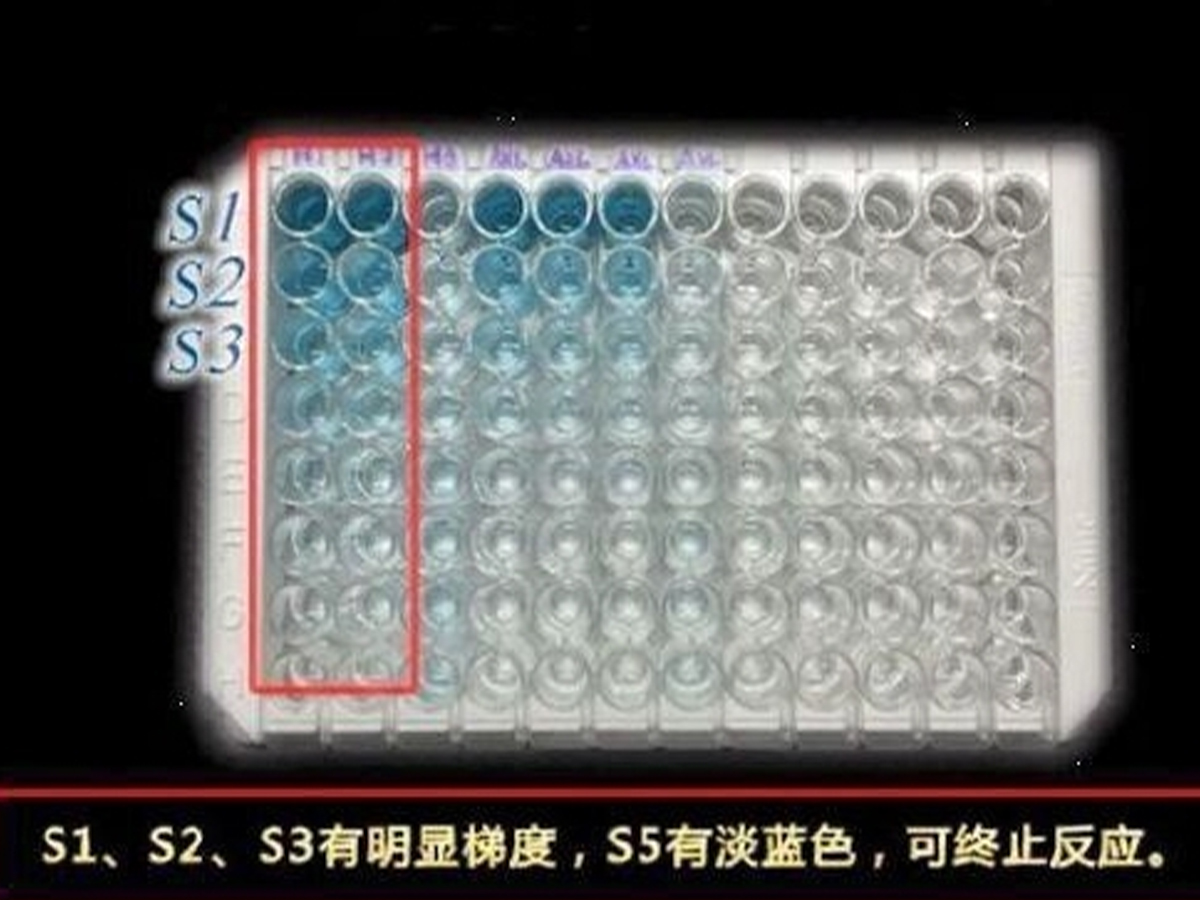
检测原理:本试剂盒采用双抗体夹心酶联免疫吸附检测技术。特异性抗人CCL5抗体预包被在高亲和力的酶标板上。酶标板孔中加入标准品、待测样本和生物素化的检测抗体,经过孵育,样本中存在的CCL5与固相抗体和检测抗体结合。洗涤去除未结合的物质后,加入辣根过氧化物酶标记的链霉亲和素(Streptavidin-HRP)。洗涤后,加入显色底物TMB,避光显色。颜色反应的深浅与样本中CCL5的浓度成正比。加入终止液终止反应,在450 nm波长(参考波长570 - 630 nm)测定吸光度值。
分子信息
CCL5 分子靶点信息概述
- 分子名:CCL5, C-C motif chemokine ligand 5
- 基因家族:Chemokine ligands
- 别名:RANTES; SISd; TCP228; MGC17164
- 曾用名:D17S136E; SCYA5
- 全称:T-cell specific protein p288; T-cell specific RANTES protein; SIS-delta; regulated upon activation, normally T-expressed, and presumably secreted; beta-chemokine RANTES; small inducible cytokine subfamily A (Cys-Cys), member 5; small inducible cytokine A5 (RANTES); chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5
CCL5 分子靶点综述
趋化因子配体5(CCL5),又名RANTES,是一种趋化细胞因子。它可趋化T细胞、嗜酸性粒细胞和嗜碱性粒细胞,在招募白细胞到炎症位点发挥着积极的作用。在T细胞释放的细胞因子如IL-2和IFN-γ的帮助下,CCL5可诱导某些自然杀伤细胞(NK)增殖和活化形成CC趋化因子活化的杀伤(CHAK)细胞。CCL5也是一种由CD8+T细胞释放的HIV抑制因子。最近,研究者正在开发完善乳酸菌体内产生CCL5的方案,以期其成为抑制HIV进入的局部杀菌剂。
人 Human CCL5 分子靶点信息
- 分子名:CCL5, C-C motif chemokine ligand 5
- 别称:
- beta-chemokine RANTES
- C-C motif chemokine 5
- chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5
- D17S136E
- eoCP
- eosinophil chemotactic cytokine
- MGC17164
- RANTES
- regulated upon activation, normally T-expressed, and presumably secreted
- SCYA5
- SIS-delta
- SISd
- small inducible cytokine A5 (RANTES)
- small inducible cytokine subfamily A (Cys-Cys), member 5
- small-inducible cytokine A5
- t cell-specific protein P228
- T-cell specific protein p288
- T-cell-specific protein RANTES
- TCP228
- 基因序列:NCBI_Gene: 6352
- 蛋白序列:UniProtKB: P13501
人 Human CCL5靶点分子功能(预测)
Enables several functions, including enzyme activator activity; phosphatidylinositol phospholipase C activity; and signaling receptor binding activity. Involved in several processes, including cellular response to cytokine stimulus; positive regulation of cell migration; and positive regulation of cell-cell adhesion. Acts upstream of or within positive regulation of T cell migration. Predicted to be located in cytoplasm. Predicted to be active in extracellular space. Implicated in several diseases, including hepatitis B; hepatitis C; liver disease (multiple); pulmonary tuberculosis; and severe acute respiratory syndrome. Biomarker of several diseases, including fatty liver disease (multiple); glucose metabolism disease (multiple); hypertension (multiple); liver cirrhosis (multiple); and lung disease (multiple).
引用文献统计
该产品被引用的文献总数为:0
暂无相关文献引用。
ELISA标准品操作常见问题查看更多ELISA标准品操作步骤技术文章
查看更多ELISA标准品操作步骤技术文章
操作步骤
文章目录[隐藏]
- ELISA操作常见问题
- 小心!你的 ELISA 试剂盒可能是假的
- 开学学习计划,如何收集ELISA检测样本——细胞
- 开学学习计划,如何选择ELISA试剂盒
- 开学学习计划,ELISA从新手到入门!
- 一文掌握ELISA实验显色判断、数据分析及标曲拟合
- 血清OR血浆,哪个是ELISA的菜
- ELISA通关必备丨数据篇丨标准曲线不佳
- ELISA通关必备丨操作篇丨常见问题及解决方案
- ELISA通关必备丨操作篇丨溶解与稀释标准品
- ELISA通关必备丨样本篇丨不常见样本
- ELISA通关必备丨样本篇丨常见样本丨细胞
- ELISA通关必备丨如何选择试剂盒
- ELISA通关必备丨基础知识
- 真?假?ELISA试剂盒选择要小心
- ELISA常见类型一 | 双抗夹心法,你要的都在这里!
- ELISA常见类型二 | 竞争法,五分钟搞定!
- 叮!联科向您投递了个ELISA实验操作干货包,请查收~
- 【视频】ELISA实验操作步骤演示视频教程
- ELISA 组织样本的处理—大鼠组织
- 【视频】ELISA实验原理与常见问题分析
- 查看更多ELISA操作相关问题
ELISA操作常见问题
查看更多ELISA操作相关问题
引用文献
文章目录[隐藏]
- Endothelial cells promote triple-negative breast cancer cell metastasis via PAI-1 and CCL5 signaling
- Periodontal inflammation recruits distant metastatic breast cancer cells by increasing myeloid-derived suppressor cells
- The combined action of monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells and mucosal-associated invariant T cells promotes the progression of cervical cancer
- β-Adrenoceptor regulates contraction and inflammatory cytokine expression of human bladder smooth muscle cells via autophagy under pathological hydrostatic pressure
- Cytokine antibody array-based analysis of IL-37 treatment effects in asthma
- CCR5/CCR5 ligand-induced myeloid-derived suppressor cells are related to the progression of endometriosis
- Metabolic Enzyme Triosephosphate Isomerase 1 and Nicotinamide Phosphoribosyltransferase, Two Independent Inflammatory Indicators in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Evidences From Collagen-Induced Arthritis and Clinical Samples
- FABP6 Expression Correlates with Immune Infiltration and Immunogenicity in Colorectal Cancer Cells
- Increased Expression of Mitochondrial UQCRC1 in Pancreatic Cancer Impairs Antitumor Immunity of Natural Killer Cells via Elevating Extracellular ATP
- FAP-α+ immunofibroblasts in oral lichen planus promote CD4+ T-cell infiltration via CCL5 secretion
- circCYP24A1 facilitates esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression through binding PKM2 to regulate NF-κB-induced CCL5 secretion
- Changes in peripheral blood cytokines in patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome
- Impaired myeloid-derived suppressor cells are associated with recurrent implantation failure: A case-control study
- The kinase activity of integrin-linked kinase regulates cellular senescence in gastric cancer
- Monocytes Undergo Functional Reprogramming to Generate Immunosuppression through HIF-1α Signaling Pathway in the Late Phase of Sepsis
- STING agonist cGAMP enhances anti-tumor activity of CAR-NK cells against pancreatic cancer
- CCL5 promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of circulating tumor cells in renal cancer
- Role of Chemotaxis of Vδ2 T Cells to the Synovium in the Pathogenesis of Acute Gouty Arthritis
- MiR-9 promotes G-MDSC recruitment and tumor proliferation by targeting SOCS3 in breast cancer
- NAMPT/SIRT1 Expression Levels in White Blood Cells Differentiate the Different Rheumatoid Arthritis Subsets: An Inspiration from Traditional Chinese Medicine
- Original research: Chordoma recruits and polarizes tumor-associated macrophages via secreting CCL5 to promote malignant progression
- CCR5/CCR5 Ligand-Induced Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Are Related to the Progression of Endometriosis
- FAP-α + immunofibroblasts in oral lichen planus promote CD4 + T-cell infiltration via CCL5 secretion
Endothelial cells promote triple-negative breast cancer cell metastasis via PAI-1 and CCL5 signaling
Periodontal inflammation recruits distant metastatic breast cancer cells by increasing myeloid-derived suppressor cells
The combined action of monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells and mucosal-associated invariant T cells promotes the progression of cervical cancer
β-Adrenoceptor regulates contraction and inflammatory cytokine expression of human bladder smooth muscle cells via autophagy under pathological hydrostatic pressure
Cytokine antibody array-based analysis of IL-37 treatment effects in asthma
CCR5/CCR5 ligand-induced myeloid-derived suppressor cells are related to the progression of endometriosis
Metabolic Enzyme Triosephosphate Isomerase 1 and Nicotinamide Phosphoribosyltransferase, Two Independent Inflammatory Indicators in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Evidences From Collagen-Induced Arthritis and Clinical Samples
FABP6 Expression Correlates with Immune Infiltration and Immunogenicity in Colorectal Cancer Cells
Increased Expression of Mitochondrial UQCRC1 in Pancreatic Cancer Impairs Antitumor Immunity of Natural Killer Cells via Elevating Extracellular ATP
FAP-α+ immunofibroblasts in oral lichen planus promote CD4+ T-cell infiltration via CCL5 secretion
circCYP24A1 facilitates esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression through binding PKM2 to regulate NF-κB-induced CCL5 secretion
Changes in peripheral blood cytokines in patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome
Impaired myeloid-derived suppressor cells are associated with recurrent implantation failure: A case-control study
The kinase activity of integrin-linked kinase regulates cellular senescence in gastric cancer
Monocytes Undergo Functional Reprogramming to Generate Immunosuppression through HIF-1α Signaling Pathway in the Late Phase of Sepsis
STING agonist cGAMP enhances anti-tumor activity of CAR-NK cells against pancreatic cancer
CCL5 promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of circulating tumor cells in renal cancer
Role of Chemotaxis of Vδ2 T Cells to the Synovium in the Pathogenesis of Acute Gouty Arthritis
MiR-9 promotes G-MDSC recruitment and tumor proliferation by targeting SOCS3 in breast cancer
NAMPT/SIRT1 Expression Levels in White Blood Cells Differentiate the Different Rheumatoid Arthritis Subsets: An Inspiration from Traditional Chinese Medicine
Original research: Chordoma recruits and polarizes tumor-associated macrophages via secreting CCL5 to promote malignant progression
- 腹腔积液 血浆
CCR5/CCR5 Ligand-Induced Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Are Related to the Progression of Endometriosis
- 细胞培养上清
FAP-α + immunofibroblasts in oral lichen planus promote CD4 + T-cell infiltration via CCL5 secretion